Electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) can cause various side effects, including:
- Muscle injuries such as fiber splitting or degeneration.
- Electrical hazards, including shocks and burns from faulty devices.
- Skin irritation, bruising, or burns at electrode sites.
- Sensory effects, such as temporary tingling, dizziness, or nausea.
Users should be cautious of contraindications, including cardiac devices and active vascular conditions. Understanding these risks is essential for safe use. Further details on precautions and effectiveness can enhance user safety.
Key Takeaways
- Common side effects include skin irritation, redness, and bruising at electrode sites due to improper use or excessive pressure.
- Temporary muscle soreness may mimic post-exercise discomfort but is generally non-harmful.
- Users may experience dizziness and nausea, though these side effects are less common.
- Excessive muscle stimulation can lead to serious conditions like rhabdomyolysis and muscle fiber injury.
- Immediate discontinuation is crucial if unusual symptoms occur during EMS sessions.
Muscle and Tissue Risks
Electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) pose significant risks to muscle and tissue health when improperly used. The improper application can lead to excessive muscle tension, resulting in potential muscle damage and tissue inflammation. Key risks include:
- Muscle Fiber Injury: Overuse can cause structural damage, such as fiber splitting and degeneration.
- Inflammatory Responses: EMS may trigger localized inflammation, with immune cells infiltrating damaged areas, leading to myositis.
- Rhabdomyolysis: This severe condition arises from excessive muscle breakdown, potentially harming kidney function.
- Reduced Muscle Force: Users may experience a significant reduction in muscle force lasting several days post-application.
Understanding these risks is essential for safe and effective EMS use, promoting muscle health and preventing injury.
Electrical and Device-Related Hazards

The use of electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) carries inherent risks beyond muscle and tissue concerns.
Electrical Hazards
- EMS devices can cause shocks and burns if cables and leads fail to meet electrical safety standards.
- There exists a risk of electrocution when equipment is improperly designed or maintained.
- EMS may interfere with implanted devices, such as pacemakers.
Device-Related Issues
- Poor design and inadequate instructions can lead to misuse and injuries.
- Cables and leads must comply with safety standards to prevent electrocution risks.
- User error can result in burns or shocks, emphasizing the need for proper device maintenance.
Adhering to FDA regulations and ensuring clear instructions are critical for safe EMS operation.
Contraindications and Population-Specific Warnings

When considering the use of electronic muscle stimulators, it is crucial to acknowledge various contraindications and population-specific warnings to guarantee safety and efficacy.
Cardiovascular Considerations:
- Absolute contraindications include pacemaker and cardiac defibrillator wearers.
- Patients with arrhythmias or impaired heart conduction require close medical supervision.
- Avoid use in active deep vein thrombosis or severe peripheral vascular diseases.
Neurological Precautions:
- Epileptic individuals should avoid stimulation due to seizure risks.
- Caution is advised near critical nerves and reflex centers, such as the carotid sinus.
- Those with cognitive impairments may struggle to communicate adverse effects.
These considerations are essential for ensuring the safe application of electronic muscle stimulators within specific populations.
Skin and Sensory Side Effects
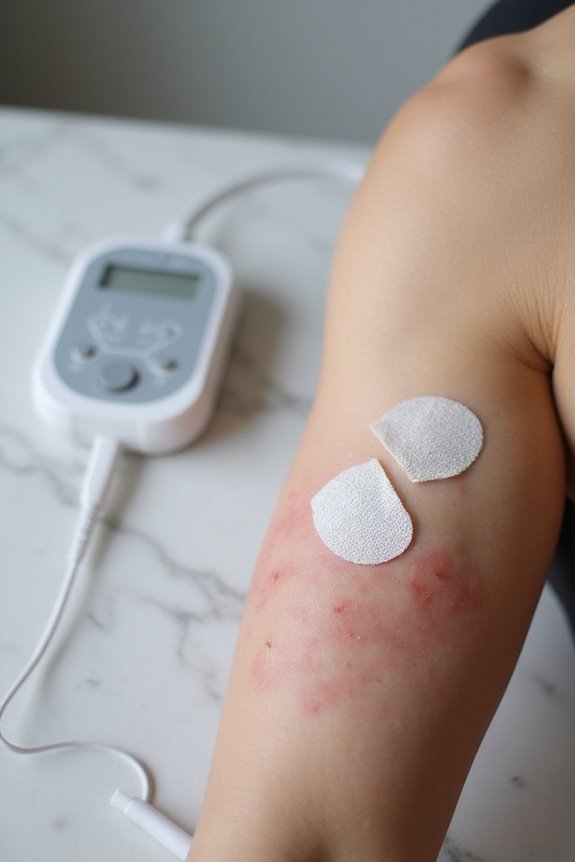
Skin and sensory side effects are notable considerations for users of muscle stimulators, as they can impact the overall experience and effectiveness of the treatment.
Skin Irritation:
- Redness and Irritation: Common at electrode sites, particularly for sensitive individuals.
- Bruises and Burns: Can occur from improper use or excessive pressure.
- Erythema and Petechia: May arise from specific techniques like iontophoresis.
Sensory Discomfort:
- Tingling Sensation: Temporary and generally non-harmful during treatment.
- Muscle Soreness: Similar to post-exercise discomfort.
- Fatigue and Headaches: Reported by some users, particularly with broader devices.
- Dizziness and Nausea: Less common but documented in certain cases.
Awareness of these effects allows users to take necessary precautions for a safer experience.
Effectiveness and Misconceptions

Understanding the effectiveness of electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) requires a nuanced perspective on their application and limitations.
EMS Benefits
- EMS can enhance muscle thickness and strength, with increases reported at 22-26% in specific muscle groups.
- Whole-body EMS (WB-EMS) shows positive effects on muscle mass, fat loss, and power, as verified by systematic reviews.
User Perceptions
- Many users mistakenly believe EMS can replace cardiovascular exercise for fat loss.
- Effective body composition changes often depend on integrating EMS with traditional training.
- While EMS supports muscle activation, claims of it being a standalone solution lack scientific backing.
Professional Use and Safety Measures
Ensuring safe and effective use of electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) in professional settings necessitates a thorough approach.
Trainer Qualifications
Licensed and experienced trainers must supervise EMS sessions, ensuring participant safety through monitoring and assessments.
Equipment Standards
Utilizing FDA-approved EMS devices is essential. Regular inspections should verify that equipment remains in good condition, in compliance with safety regulations.
Monitoring and Emergency Protocols
Trainers should maintain visual contact, checking for participant distress. Intensity levels must be adjusted throughout the session to minimize adverse effects. Emergency procedures should be established, including a brief on the device’s shutdown function.
Environmental Considerations
EMS should not be used in humid conditions or near water, and all jewelry must be removed to reduce risks. Proper usage of EMS devices can lead to improved quality of life for individuals with chronic pain conditions.
Common Side Effects of EMS
The use of electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) carries a range of common side effects that may arise during or after application.
Muscle Soreness and Damage
- Similar to traditional workouts, muscle soreness can occur, especially in beginners or after high-intensity use.
- Elevated creatine-kinase (CK) levels may be observed post-treatment, indicating muscle stress.
Skin Irritation and Burns
– Adhesive pads may cause localized irritation or burns, particularly with excessive intensity.
Overstimulation and Muscle Fatigue****
– Excessive use can lead to muscle fatigue or sharp pain, necessitating regulated intensity.
Electrolyte Imbalance and Hydration Concerns
– Intensive EMS sessions can disrupt electrolyte balance, impacting muscle recovery and increasing fatigue.
Monitoring these side effects is essential for effective soreness management and overall safety during EMS use.
Long-Term Considerations
Long-term considerations associated with electronic muscle stimulators (EMS) warrant careful examination, particularly regarding their potential impacts on muscle tissue and overall health.
- Muscle Damage: Repeated EMS can elevate serum creatine kinase (CK) levels considerably, indicating muscle fiber breakdown.
- Muscle Adaptation: While some adaptation may occur, with reduced CK response over time, the long-term effects remain uncertain.
- Training Frequency: High-frequency EMS use can lead to risks, including rhabdomyolysis and kidney stress, necessitating careful management of intensity.
- Muscle Imbalances: Uneven application may result in muscle imbalances, affecting posture and increasing injury risk.
- Skin Effects: Chronic application can provoke skin irritation or burns, emphasizing the importance of proper electrode care and monitoring.
Monitoring and evaluation are essential for safe long-term use.
Recommendations for Safe Use
How can users guarantee the safe application of electronic muscle stimulators (EMS)? Adhering to established safety protocols is vital. Users should:
- Avoid EMS if they have implanted cardiac devices, malignancies, or open wounds.
- Consult healthcare professionals if pregnant or experiencing conditions like epilepsy or cognitive impairment.
- Confirm continuous monitoring by trained professionals during sessions to observe for adverse reactions.
- Maintain close trainer-participant proximity with clear communication regarding impulse intensity.
- Follow thorough user instructions to confirm proper device use and electrode placement.
User education is key; consumers must verify FDA clearance for EMS devices and conduct regular maintenance checks. Immediate discontinuation of EMS is necessary if unusual symptoms occur, confirming participant safety remains a priority.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Use EMS Devices While Exercising?
Using EMS devices during exercise can enhance muscle activation and strength, promoting exercise benefits. However, ensuring EMS safety through proper guidance and adherence to manufacturer instructions is vital to avoid potential risks and adverse effects.
How Often Can I Use an EMS Device?
The recommended usage frequency for EMS devices is 2 to 3 times weekly, adhering to safety guidelines that guarantee effective muscle recovery and performance. Personalized adjustments may enhance benefits, fostering a supportive environment for individual progress.
Are There Specific Brands of EMS Devices Recommended?
In the domain of device features, brand comparisons reveal top picks like Therabody and Beurer, celebrated for their innovative designs. Users appreciate tailored programs and effective muscle relief, fostering a sense of community among wellness enthusiasts.
What Should I Do if I Experience Pain During Use?
When experiencing pain during use, individuals should prioritize pain management by adjusting device settings. Gradually increasing intensity and ensuring proper electrode placement can alleviate discomfort, fostering a safe and supportive environment for effective muscle stimulation.
Can EMS Devices Improve Athletic Performance?
The effectiveness of EMS devices for athletic performance enhancement remains mixed. While they may aid in muscle recovery, their overall impact on strength and explosive capabilities is limited, positioning them as supplementary rather than primary training tools.





